ADF Logging Explained Chapter 3
This post illustrates ADFLogger initialization concepts.First thing you create the ADF Logger instance using below code :
private static ADFLogger logger = ADFLogger.createADFLogger(TestLoggerTFBean.class);
Log Level for newly Created Instance
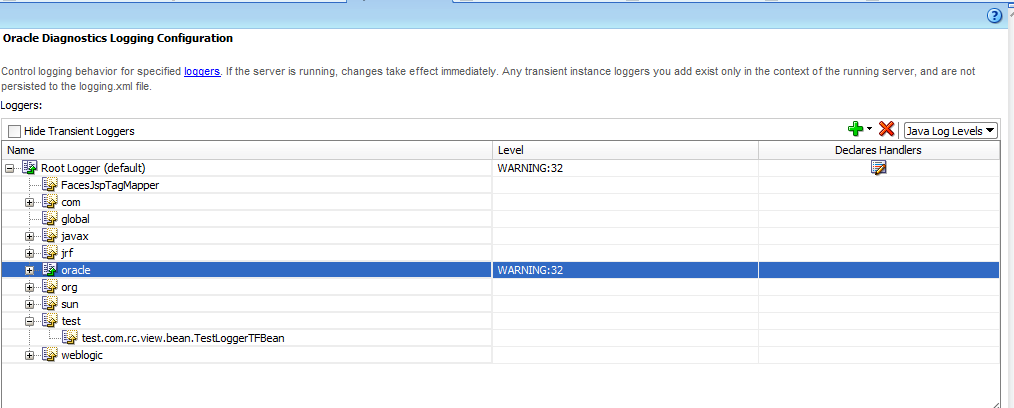
I ask you a very simple question : Say you have not done any additional change to Oracle Diagnostic Logging. That is it looks like this :Now What is the logLevel for the above ADFLogger instance "logger" ?
Answer is LogLevel is null.
How isLoggable(Level level) check works on logger instance with LogLevel null ?
Ahh...Now we know that LogLevel is null for a newly created ADFLogger instance when it is not configured in OracleDiagnostic Logging. Wondering what will happen to code comparing LogLevel before logging any info ? Like :
if(logger.isLoggable(ADFLogger.INTERNAL_ERROR)){
logger.log("loggingBtnAction logger.isLoggable(ADFLogger.INTERNAL_ERROR) -> logger.log ");
}
Well ADFLogger is based on java.util.logging.Logger and isLoggable method works on class variable levelValue [ private volatile int levelValue ] defined in java.util.logging.Logger . When a new ADFLogger instance is created, levelValue variable is update using the below logic :
So if LogLevel for logger is null it means that logLevel is inherited from the parent. As the logger build a tree, it picks the logLevel of parent till it reaches the logger which returns a level not null.
From java.util.logging.Logger
private volatile int levelValue; // current effective level value
Thanks to Timo Hahn for clarifying this on https://community.oracle.com/thread/3524267